Sep 17, 2023The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands.
What is Glycosidic Bond in DNA and RNA?
The four nitrogen bases found in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Each of these bases are often abbreviated a single letter: A (adenine), C (cytosine), G (guanine), T (thymine). The bases come in two categories: thymine and cytosine are pyrimidines, while adenine and guanine are purines (). The pyrimidine structure is produced

Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
The sugar found in DNA is called deoxyribose. If it sounds familiar, that’s because it’s not coincidentally the “D” in “DNA” – deoxyribonucleic acid. In terms of chemical structure, deoxyribose is constructed of five carbon, ten hydrogen, and four oxygen (C5H10O4).

Source Image: forum.thefreedictionary.com
Download Image
DNA Structure, Function, Types, and Its Discovery
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. The important components of each nucleotide are a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate group (see Figure 1). Each nucleotide is named depending on its nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be a purine, such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or a pyrimidine, such as

Source Image: biosynth.com
Download Image
What Sugar Is Found In The Dna
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. The important components of each nucleotide are a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate group (see Figure 1). Each nucleotide is named depending on its nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be a purine, such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or a pyrimidine, such as
The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA. For example, the sequence ATCGTT might instruct for blue eyes, while ATCGCT might instruct for brown.
Nucleosides and Nucleotides Toolbox Part 1″ Now Available! | Blog | Biosynth
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
Analyzing the Components of the Structure of DNA Practice | Biology Practice Problems | Study.com

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Plant Life: RNA
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.

Source Image: lifeofplant.blogspot.com
Download Image
What is Glycosidic Bond in DNA and RNA?
Sep 17, 2023The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands.

Source Image: biologyexams4u.com
Download Image
DNA Structure, Function, Types, and Its Discovery
The sugar found in DNA is called deoxyribose. If it sounds familiar, that’s because it’s not coincidentally the “D” in “DNA” – deoxyribonucleic acid. In terms of chemical structure, deoxyribose is constructed of five carbon, ten hydrogen, and four oxygen (C5H10O4).
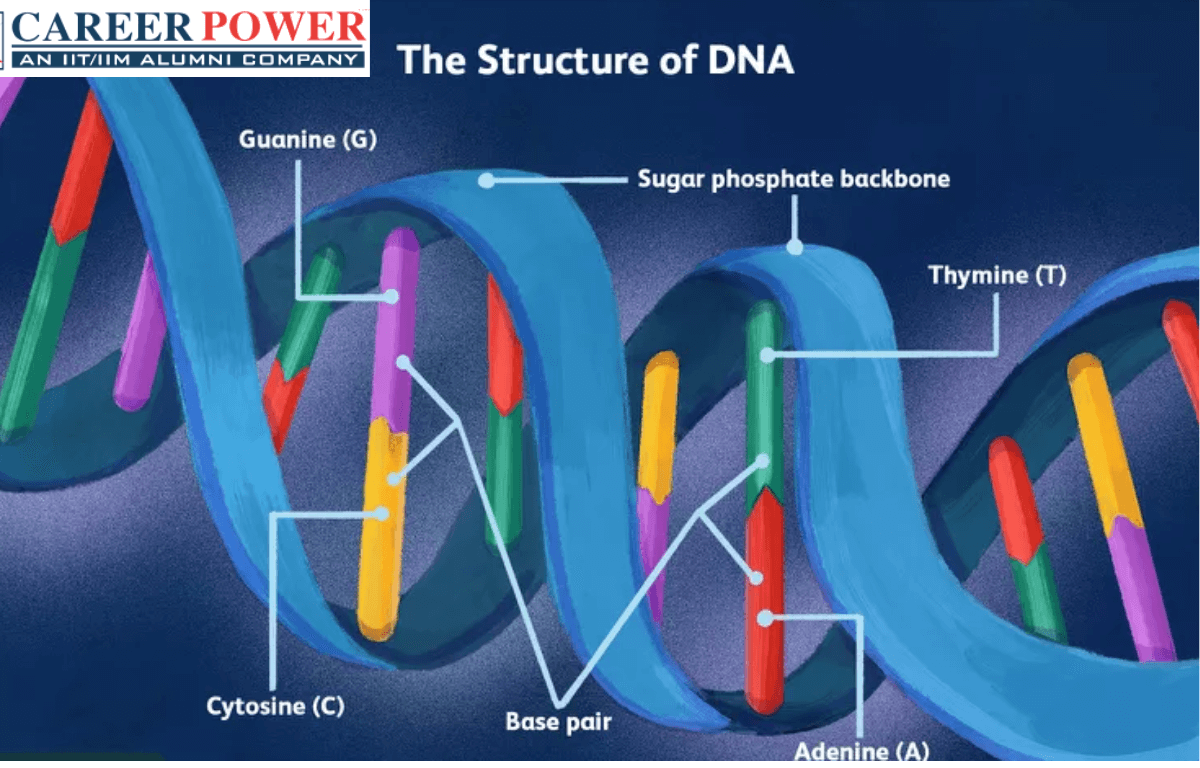
Source Image: careerpower.in
Download Image
DNA structure: Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function | Osmosis
Identify the sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base, 5′ and 3′ carbons in a nucleotide and the key difference between DNA and RNA. Explain the structure of the double helix, including the role of hydrogen bonds and covalent (phosphodiester) bonds. Explain why the abundance of A is roughly equal to T and G is roughly equal to C in DNA.

Source Image: osmosis.org
Download Image
List of Vocabulary Terms for High School Biology – How She Teaches
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. The important components of each nucleotide are a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate group (see Figure 1). Each nucleotide is named depending on its nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be a purine, such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or a pyrimidine, such as

Source Image: howsheteaches.com
Download Image
Sugar – Definition and Examples – Biology Online Dictionary
The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA. For example, the sequence ATCGTT might instruct for blue eyes, while ATCGCT might instruct for brown.
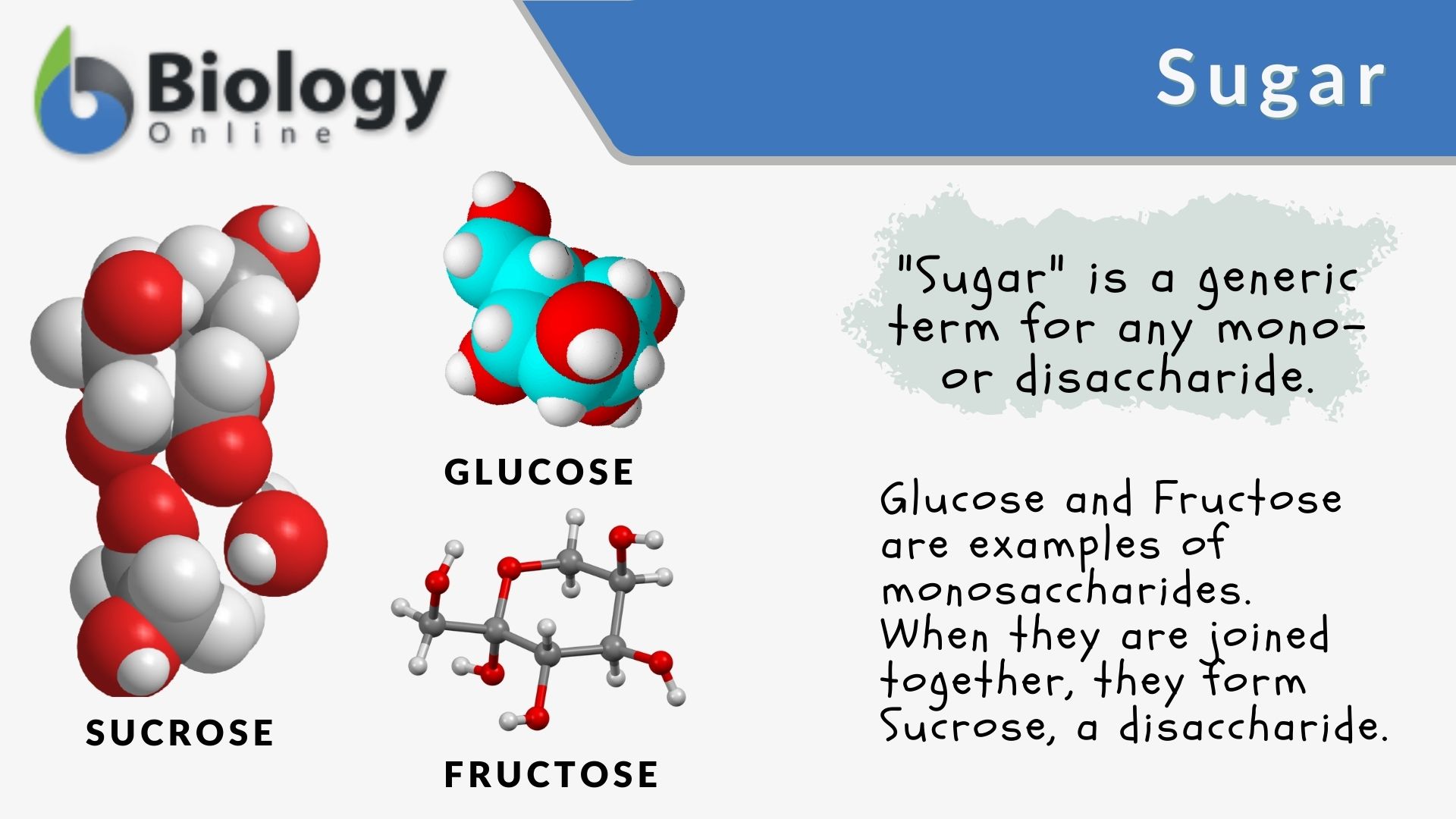
Source Image: biologyonline.com
Download Image
Plant Life: RNA
Sugar – Definition and Examples – Biology Online Dictionary
The four nitrogen bases found in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Each of these bases are often abbreviated a single letter: A (adenine), C (cytosine), G (guanine), T (thymine). The bases come in two categories: thymine and cytosine are pyrimidines, while adenine and guanine are purines (). The pyrimidine structure is produced
DNA Structure, Function, Types, and Its Discovery List of Vocabulary Terms for High School Biology – How She Teaches
Identify the sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base, 5′ and 3′ carbons in a nucleotide and the key difference between DNA and RNA. Explain the structure of the double helix, including the role of hydrogen bonds and covalent (phosphodiester) bonds. Explain why the abundance of A is roughly equal to T and G is roughly equal to C in DNA.